This self-paced course will help you prepare for the Azure Developer certification exam AZ-204: Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure.



Prevents you from committing passwords and other sensitive information to a git repository.
git-secrets scans commits, commit messages, and --no-ff merges to prevent adding secrets into your git repositories. If a commit, commit message, or any commit in a --no-ff merge history matches one of your configured prohibited regular expression patterns, then the commit is rejected.
git-secrets must be placed somewhere in your PATH so that it is picked up by git when running git secrets.
Linux/Unix OS:
You can use the install target of the provided Makefile to install git secrets and the man page. You can customize the install path using the PREFIX and MANPREFIX variables.
make install
Windows OS :
Run the provided install.ps1 powershell script. This will copy the needed files to an installation directory (%USERPROFILE%/.git-secrets by default) and add the directory to the current user PATH.
PS > ./install.ps1
MacOS :
Run the below command to install the git secrets on the mac machine .
brew install git-secrets
--install :Installs git hooks for a repository. Once the hooks are installed for a git repository, commits and non-fast-forward merges for that repository will be prevented from committing secrets.
--scan : Scans one or more files for secrets. When a file contains a secret, the matched text from the file being scanned will be written to stdout and the script will exit with a non-zero status. If no files are provided, all files returned by git ls-files are scanned.
--scan-history: Scans repository including all revisions. When a file contains a secret, the matched text from the file being scanned will be written to stdout and the script will exit with a non-zero status.
--list: Lists the git-secrets configuration for the current repo or in the global git config.
--add :Adds a prohibited or allowed pattern.
--add-provider: Registers a secret provider. Secret providers are executables that when invoked output prohibited patterns that git-secrets should treat as prohibited.
--register-aws:Adds common AWS patterns to the git config and ensures that keys present in ~/.aws/credentials are not found in any commit.
--register-azure:Adds common AZURE patterns to the git config and ensures that keys present in ~/.azure/credentials are not found in any commit.
-f, --force: Overwrites existing hooks if present while installation of git secrets.
-r, --recursive :Scans the given files recursively. If a directory is encountered, the directory will be scanned. If -r is not provided, directories will be ignored.
--cached:Searches blobs registered in the index file.
--no-index :Searches files in the current directory that is not managed by git.
--untracked :In addition to searching in the tracked files in the working tree.

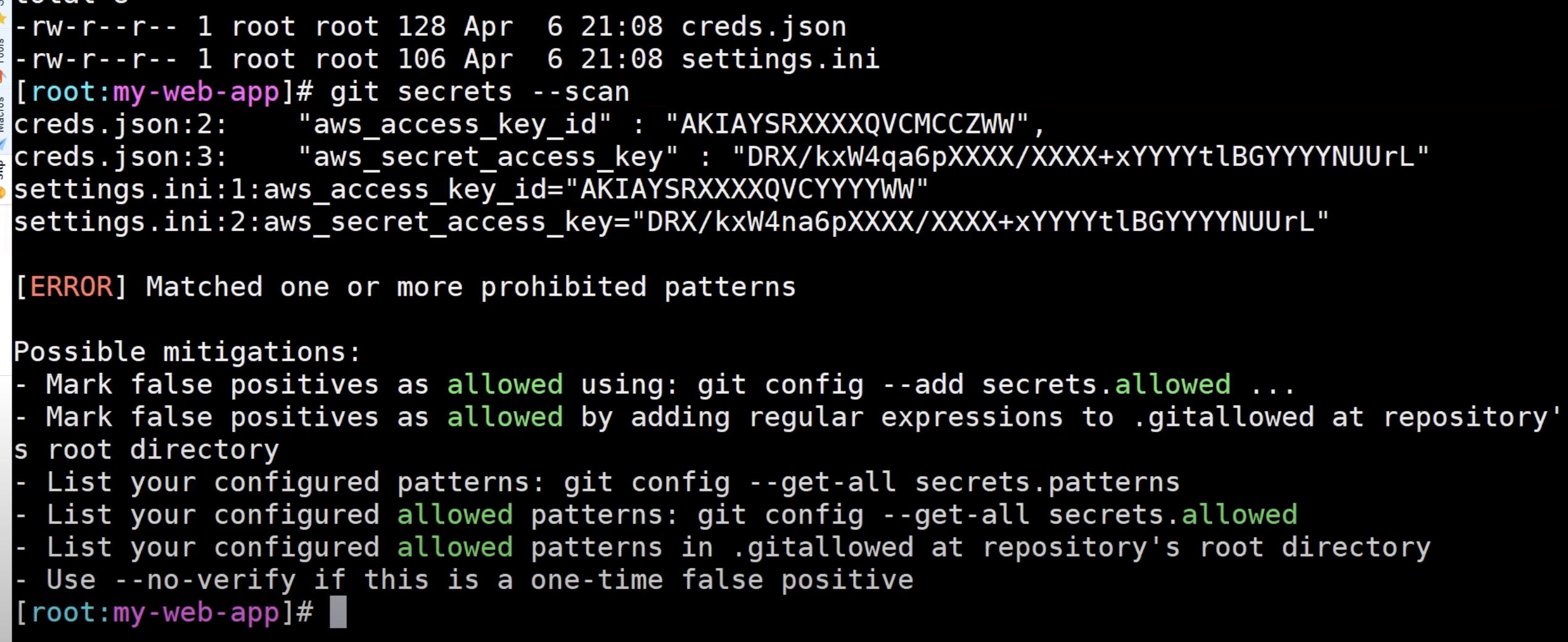
2. Once after the installation is completed , then we need to start the scanning of our repository before we checkin the code .
Depending upon the secrets it will throw us the error , if we did not get any error then we can commit it accordingly.
3. By this way we can even add it as part of our CICD pipeline so that even during our code build it scans and then shows us the error .

We also have a lot of code scanning tools like this to detect the secrets in our code such as :
Gittyleaks
Secrets Scanning
Git Secrets
Repo Supervisor
Truffle Hog
Git Hound
Gitrob
Watchtower
Repo Security Scanner
GitGuardian
In our next topic , we will see the same secrets scanning using Truffle Hog .

This self-paced course will help you prepare for the Azure Developer certification exam AZ-204: Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure.
You said: git-secrets must be placed somewhere in your PATH so that it is picked up by git when running git secrets.
I have 2 questions:
1. Do you have any examples or screenshot how to do that?
2. Let’s say my repo is having a python script having AWS key and few hardcoded passwords for few usernames. Will it detect if
2.1 its in untracked mode
2.2 its in staging area
2.3 its just committed locally
Because I went to that repo and tried `brew install git-secrets` and then ran git secrets –scan
It didn’t give any result/output?
What might have went wrong?